$350.00 – $4,000.00Price range: $350.00 through $4,000.00
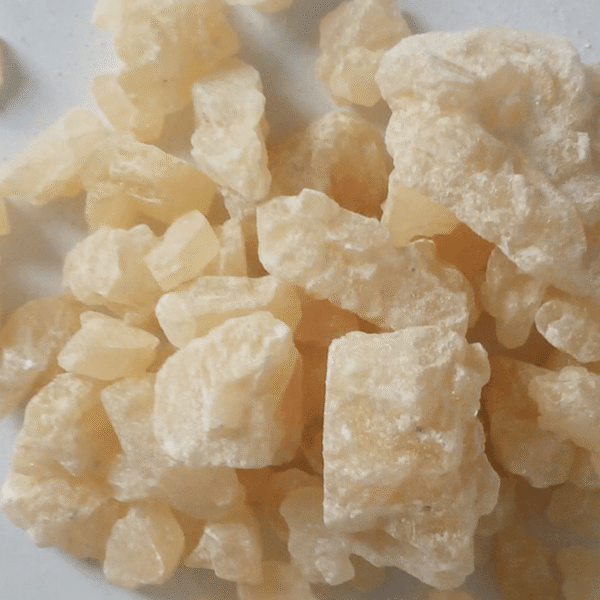
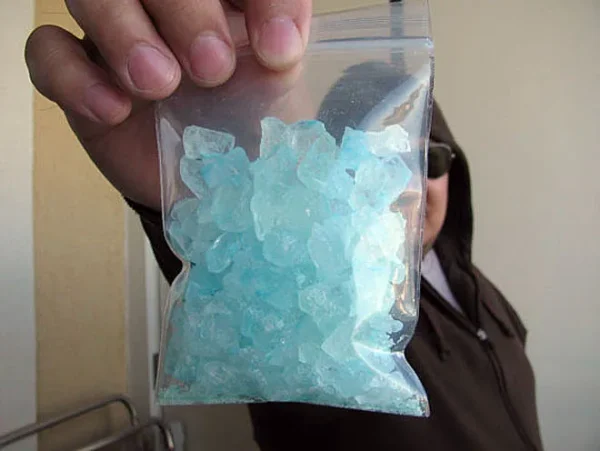
Ox gallstones, known in tradition Chinese medicine as calculus bovis or niu-huang, are natural formations derived from the bile of cattle. Historically, they have been valued not only for their therapeutic properties but also for their symbolic association with purity and health. The careful extraction and preparation of ox gallstones ensure their efficacy as a medicinal agent, reflecting centuries of traditional practice.
In Chinese herbology, ox gallstones are considered a potent remedy. They are traditionally used to balance the body’s energy (qi) and support detoxification. Practitioners often incorporate them into herbal formulations for a wide range of ailments, emphasizing a holistic approach that addresses root causes rather than merely alleviating symptoms.
Ox gallstones (niu dan in Mandarin) have held an esteemed place in Chinese medicine for centuries. Revered for both medicinal and symbolic reasons, these stones are thought to contain essential elements that support bodily functions, including liver health and detoxification. Historically, they were particularly prized during the Ming and Qing dynasties, appearing in royal pharmacopoeias and regarded as a luxury item. Today, their use persists due to renewed interest in natural remedies and holistic wellness.
Ox gallstones have been used traditionally to address a variety of health conditions, including:
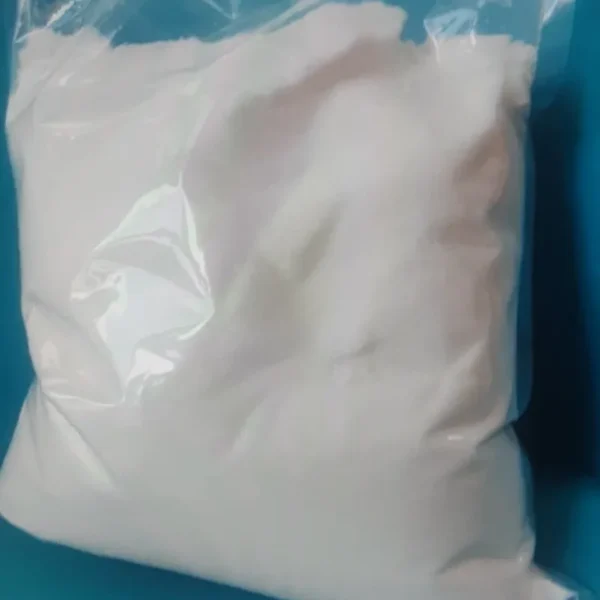
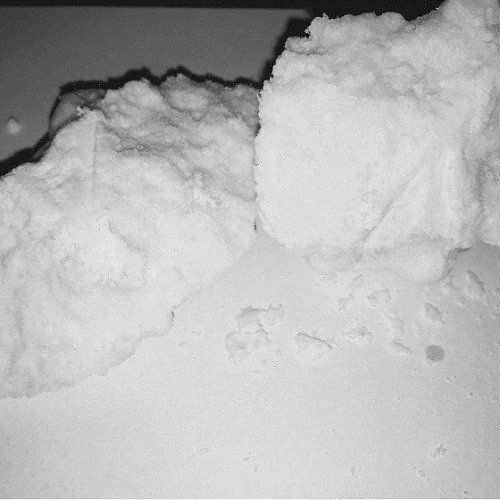
Typically, the stones are ground into a fine powder and incorporated into herbal formulations to enhance efficacy. Dosage and preparation are guided by traditional practitioners according to patient-specific needs.
Chemically, ox gallstones are composed of bile acids, cholesterol, and other bioactive compounds. Modern research has explored their potential hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidative properties. Some studies suggest that components of ox gallstones may support liver function and contribute to detoxification.
However, rigorous clinical evidence remains limited. Much of the current data comes from in vitro or animal studies, making direct application to humans uncertain. Critics advocate for standardized extraction methods, controlled clinical trials, and careful regulatory oversight to ensure safety and validate traditional claims.
While ox gallstones are highly valued in traditional medicine, caution is warranted. Potential risks include:
Practitioners emphasize proper dosing, careful preparation, and ethical sourcing to mitigate potential issues.
Ox gallstones represent a bridge between traditional knowledge and modern integrative medicine. As interest in natural remedies grows, further research could clarify the active compounds, optimal usage, and potential therapeutic applications. Investigating their biochemical properties, safety profile, and efficacy may pave the way for wider acceptance in contemporary healthcare settings.
Ox gallstones hold enduring significance in traditional Chinese medicine, valued for their detoxifying, healing, and restorative properties. While scientific validation is ongoing, their historical and cultural importance, combined with preliminary research insights, positions them as a noteworthy component in both traditional and modern approaches to wellness.